Revelation 20:7-9
And when the thousand years are completed, Satan will be released from his prison, 8 and will come out to deceive the nations which are in the four corners of the earth, Gog and Magog, to gather them together for the war; the number of them is like the sand of the seashore. 9 And they came up on the broad plain of the earth and surrounded the camp of the saints...
NASB
From: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Golden_Horde
Golden Horde
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- This article refers to the medieval Turkic state. For the Irish rock band, see The Golden Horde (band).
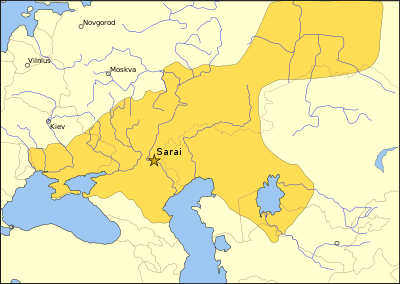
The Golden Horde (Mongolian: Алтан Ордын улс Altan Ordyn Uls; Tatar: Altın Urda; Russian: Золотая Орда, Zolotaya Orda; Turkish: Altın Ordu) is a Russian designation for the Mongol[1][2][3] — later Turkicized[4] — khanate established in the western part of the Mongol Empire after the Mongol invasion of Rus in the 1240s: present-day Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, Kazakhstan, and the Caucasus. At its peak the Golden Horde's territory included most of Eastern Europe from the Urals to the right banks of the Dniper River, extending east deep into Siberia. On the south the Horde's lands bordered on the Black Sea, the Caucasus Mountains, and the territories of the Mongol dynasty known as the Il-Khans.[4]
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Name
The name Golden is believed to have come from the steppe colour system for the cardinal directions: black — north, blue — east, red — south, white — west, and yellow (or gold) — center.
According to another version, the name was derived from the Russian designation Zolotaya Orda, a magnificent golden tent camp along the Volga River that Batu Khan established to mark a place of his future capital on the Volga[5]. In Mongolian, Golden Horde (Altan Orda) means Golden Camp, or palace.[3]
Also, the Mongol ruling clan referred to themselves as the "Golden Family", which could be the origins for "The Golden Horde."[citation needed]
There are no written records dated prior to 17th century (well after the destruction) that refer to the state as Golden Horde. Earlier documents allude to this polity as Ulus of Jochi.
Some scholars prefer to use an alternative name, Kipchak Khanate (Russian designation for the Ulus Juchi), because various derivatives of Kipchak were also applied to this state in medieval documents.
[edit] Mongol origins
At his death, Genghis Khan divided the Mongol Empire amongst his four sons. Jochi was the eldest, but he was dead and his paternity was in doubt, so the westernmost lands trodden by the Mongol hoof, then southern Russia and Kazakhstan, were given to his eldest sons, Batu who eventually became the ruler of the Blue Horde; and Orda, who became the leader of the White Horde.[6][7]

In 1235, Batu (being the eldest son) with the great general Subedei began an invasion westwards, first conquering the Bashkirs and then moving on Volga Bulgaria in 1236. From here, in 1237 he conquered the southern steppes of the Ukraine, forcing the Cumans to flee westwards. Moving north, Batu began the Mongol invasion of Rus and for three years subjugated the Russian principalities, whilst his cousins Kadan and Guyuk moved southwards into Alania.
Blaming the migration of the Cumans as his Casus belli, Batu's Horde with an assortment of brothers and cousins including Shiban, Orda, Kadan and Mongke Khan continued west, raiding Poland and Hungaryand culminating in the Battles of Legnica and Muhi. In 1241, however, the Great Khan Ogedei died in Mongolia, and Batu turned back from his siege of Viennato take part in disputing the succession. The Mongol armies would never again travel so far west.
In 1242, after retreating through Hungary (And destroying Pest in the process), and subjugating Bulgaria.[8], Batu established his capital at Sarai, commanding the lower stretch of the Volga River, on the site of the Khazarian capital of Atil. Shortly before that, Batu and Orda's younger brother Shiban left Batu's army and was given his own enormous ulus east of the Ural Mountains along the Ob and Irtysh Rivers.
[edit] Golden Age
The people of the Golden Horde were mostly a mixture of Turks and Mongols. The Horde was gradually Turkified and lost its Mongol identity, while the descendants of Batu's original Mongol warriors constituted the upper class of the society.[9] Most of the Horde's population were Kypchaks, Bulgar Tatars, Kyrgyz, Khwarezmians, and other Turkic peoples. They were commonly named the Tatars by the Russians and Europeans. Russians preserved this common name for this peoples down to the 20th century, whereas the most of these peoples identified themselves with their ethnic or tribal names, some also considered themselves as simply Muslims. The most of the Muslim population, both agricultural and nomadic, adopted the Kypchak language, developed to the regional languages of Kypchak group after the Horde disintegrated.
The descendents of Batu ruled the Golden Horde from Sarai Batu and later Sarai Berke, controlling an area ranging from the Volga river to the Carpathian mountains and the mouth of the Danube, whilst the descendents of Orda ruled the area from the Ural River to Lake Balkhash.
[edit] Internal organization
The Horde's supreme ruler was the khan, chosen by the kurultai among Batu Khan's descendants. The prime minister, also ethnically Mongol, was known as "prince of princes", or beklare-bek. The ministers were called viziers. Local governors, or basqaqs, were responsible for levying tribute and extinguishing popular discontent. Civil and military administration, as a rule, was not separated.
The Horde developed as a settled rather than nomadic culture, with Sarai evolving into a populous and prosperous metropolis. In the early 14th century, the capital was moved considerably upstream to Sarai Berqe, which became one of the largest cities of the medieval world, with 600,000 inhabitants.[10]
Despite Russian efforts at proselytizing in Sarai, the Mongols clung to their traditional animist or shamanist beliefs until Uzbeg Khan (1312-41) adopted Islam as a state religion. Several Russian rulers - Mikhail of Chernigov and Mikhail of Tver among them - were reportedly assassinated in Sarai for their refusal to worship pagan idols, but the khans were generally tolerant and even freed the Russian Orthodox Church of taxes.
[edit] Vassals and allies
The Horde exacted tribute from its subject peoples - Russians, Armenians, Georgians, Circassians, Alans, Crimean Greeks, Crimean Goths, and others. The territories of Christian subjects were regarded as peripheral areas of little interest as long as they continued to pay tribute. These vassal states were never incorporated into the Horde, and Russian rulers early obtained the privilege of collecting the Tatar tribute themselves. To maintain control over Russia, Tatar warlords carried out regular punitive raids to Russian principalities (most dangerous in 1252, 1293, 1382).
There is a point of view, much propagated by Lev Gumilev, that the Horde and Russian polities concluded a defensive alliance against the fanatical Teutonic knights and pagan Lithuanians. Enthusiasts point to the fact that the Mongol court was frequented by Russian princes, notably Yaroslavl's Feodor the Black, who boasted his own ulus near Sarai, and Novgorod's Alexander Nevsky, the sworn brother of Batu's successor Sartaq Khan. Although Novgorod never acknowledged the Horde's ascendancy, a Mongol contingent supported Novgorodians in the Battle of the Ice.
Sarai carried on a brisk trade with the Genoese trade emporiums on the Black Sea littoral - Soldaia, Caffa, and Azak. Mamluk Egypt was the khans' long-standing trade partner and ally in the Mediterranean. Berke, the khan of Kipchak had drawn up an alliance with the Mamluk Sultan Baibars in 1261.[11]
[edit] Political evolution
After Batu's death in 1255, the prosperity of his empire lasted for a full century, until the assassination of Jani Beg in 1357, though the intrigues of Nogai did invoke a partial civil war in the late 1290's. The Horde's military clout peaked during the reign of Uzbeg (1312-41), whose army exceeded 300,000 warriors.
Their Russian policy was one of constantly switching alliances in an attempt to keep Russia weak and divided. In the 14th century the rise of Lithuania in North East Europe posed a challenge to Tatar control over Russia. Thus Uzbeg Khan began backing Moscow as the leading Russian state. Ivan I Kalita was granted the title of grand prince and given the right to collect taxes from other Russian potentates.
[edit] Disintegration and fall
The Black Death of the 1340s was a major factor contributing to the Golden Horde's eventual downfall. Following the disastrous rule of Jani Beg and his subsequent assassination, the empire fell into a long civil war, averaging one new Khan per annum for the next few decades (Though Orda's white horde carried on generally free from trouble until the late 1370's). By the 1380s, Khwarezm, Astrakhan, and Muscovy attempted to break free of the Horde's power, while the lower reaches of the Dnieper were annexed by Lithuania and Poland in 1368 (Whilst the eastern principalities were generally annexed with little resistance).
Mamai, a Tatar general who did not formally hold the throne, attempted to reassert Tatar authority over Russia. His army was defeated by Dmitri Donskoi at the Battle of Kulikovo in his second consecutive victory over the Tatars. Mamai soon fell from power, and in 1378, Tokhtamysh, a descendant of Orda Khan and ruler of the White Horde, invaded and annexed the territory of the Blue Horde, briefly reestablishing the Golden Horde as a dominant regional power.
After Mamai's defeat, Tokhtamysh tried to restore the dominance of the Golden Horde over Russia by attacking Russian lands in 1382. He besieged Moscow on August 23, but Muscovites beat off his storm, using firearms for the first time in Russian history.[12] On August 26, two sons of Tokhtamysh's supporter Dmitry of Suzdal, dukes of Suzdal and Nizhny Novgorod Vasily and Semyon, who were present in Tokhtamysh's forces, persuaded Muscovites to open the city gates, promising that forces would not harm the city in this case.[13] This allowed Tokhtamysh's troops to burst in and destroy Moscow, killing 24,000 people.[14]
A fatal blow to the Horde was dealt by Tamerlane, who annihilated Tokhtamysh's army, destroyed his capital, looted the Crimean trade centers, and deported the most skillful craftsmen to his own capital in Samarkand.
In the first decades of the 15th century, power was wielded by Edigu, a vizier who routed Vytautas of Lithuania in the great Battle of the Vorskla River and established the Nogai Horde as his personal demesne.
In the 1440s, the Horde was again wracked by civil war. This time it broke up into separate Khanates: Qasim Khanate, Khanate of Kazan, Khanate of Astrakhan, Kazakh Khanate, Uzbek Khanate, and Khanate of Crimea all seceding from the last remnant of the Golden Horde - the Great or Big Horde.
None of these new Khanates was stronger than Muscovite Russia, which finally broke free of Tatar control by 1480. Each Khanate was eventually annexed by it, starting with Kazan and Astrakhan in the 1550s. By the end of the century the Siberia Khanate was also part of Russia, and descendants of its ruling khans entered Russian service.
The Crimean Khanate became a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire in 1475 and subjugated what remained of the Great Horde by 1502. Crimean Tatars wreaked havoc in southern Russia, Ukraine and even Poland in the course of the 16th and early 17th centuries but they were not able to defeat Russia or take Moscow. Under Ottoman protection, the Khanate of Crimea continued its precarious existence until Catherine the Great annexed it on April 8, 1783. It was by far the longest-lived of the successor states to the Golden Horde.
[edit] Reference and notes
- ^ G. Vernadsky, M. Karpovich: "The Mongols and Russia", Yale University Press, 1953
- ^ "Empire of the Golden Horde", The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition, 2001-05.
- ^ a b T. May, "Khanate of the Golden Horde", North Georgia College and State University.
- ^ a b "Golden Horde", in Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2007. Quotation: "also called Kipchak Khanate Russian designation for the Ulus Juchi, the western part of the Mongol Empire, which flourished from the mid-13th century to the end of the 14th century. The people of the Golden Horde were a mixture of Turks and Mongols, with the latter generally constituting the aristocracy."
- ^ The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2001-05.
- ^ Edward L. Keenan, Encyclopedia Americana article
- ^ B.D. Grekov and A.Y. Yakubovski "The Golden Horde and its Downfall"
- ^ Denis Sinor, "The Mongols in the West", Journal of Asian History v.33 n.1 (1999).
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ Mantran, Robert (Fossier, Robert, ed.) "A Turkish or Mongolian Islam" in The Cambridge Illustrated History of the Middle Ages: 1250-1520, p. 298
- ^ (Russian) Dmitri Donskoi Epoch
- ^ (Russian) History of Moscow settlements - Suchevo
- ^ Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd edition, entry on "Московское восстание 1382", available online here
[edit] Further reading
- Boris Grekov and Alexander Yakubovski, "The Golden Horde and its Downfall".
- George Vernadsky, "The Mongols and Russia".
[edit] See also
- Berke-Hulagu war
- Black Death
- Cossacks
- Cumans
- Daily Life in the Mongol Empire
- Eurasians
- Islam in Europe
- List of Khans of the Golden Horde
- List of wars in the Muslim world
- Mongol invasion of Rus
- Nomadic people
- Russo-Kazan Wars
- Tatar invasions
- Timeline of the Tataro-Mongol Yoke in Russia
- Tokhtamysh-Tamerlane war
[edit] External links
| [show] Mongol Empire |
|---|